Daily Stream
A Strategic Approach of Harnessing the Power of AI
In business, the integration of artificial intelligence has become a necessity for staying competitive. However, the path to successful implementation of AI is a complex one, requiring careful consideration and a well-defined strategy. In this article, I argue that starting with a clear, inspiring vision for the future and working backwards to determine the role of AI, is the most effective and sustainable approach for organizations.
MongoDB's Transition from AGPL to SSPL
Regarding open-source databases, MongoDB has been a trusted name for organizations seeking a flexible, document-oriented NoSQL solution that could offer significant scalability and cost-effectiveness. Founded in 2007 by a trio of veterans from DoubleClick, MongoDB quickly rose to become a leading player—helping companies store and manage large volumes of data in an industry that thrived on flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
Gecko: A New Benchmark for Text-to-Image Models, with Bite
Text-to-image AI models have dazzled us with their ability to generate images based on provided textual descriptions. However, evaluating their performance has long been a contentious issue, as current methods have hidden limitations. Here, we discuss Gecko, a groundbreaking new benchmark that offers a more comprehensive assessment.
Givebutter: Streamlining Nonprofit Fundraising
As an advocate for social change with a fundraising background, I’ve seen firsthand the challenges faced by organizations, regardless of their scale, in effectively managing their campaigns. My experiences have ranged from raising funds for Greek life at George Washington University to supporting national nonprofits like TAMID. Though diverse in scope, these groups encountered a common issue: they relied on a patchwork of single-solution tools with hidden fees.
A Founder's Guide to Securing Venture Capital
With investors seeking out those rare start-ups poised for massive returns, the pressure to present an audacious vision can be overwhelming. However, understanding the Power Law of Returns and its implications for founders can provide a clear path forward.
Challenges of Consistency in AI-Generated Video Content
The video generation ecosystem has seen significant advancements, most notably OpenAI’s Sora. The tool’s fluid and realistic video capabilities captured the industry’s attention, seemingly miles ahead of competitors. However, the initial excitement surrounding its debut revealed a critical need for a closer look at the limitations and challenges faced in utilizing Sora for professional film production.
The Hidden Consequences of AI in Identity Verification
As AI technology increasingly permeates various aspects of our lives, it’s becoming an integral part of identity verification. While the convenience and speed it offers are undeniable, it’s crucial to acknowledge the unintended consequences that arise. One significant concern is the potential for sensitive information to be inadvertently revealed, infringing upon privacy.
Malaysia: The New Silicon Valleys of Southeast Asia
The US-China tech war is not only changing the global geopolitical landscape but also reshaping the semiconductor industry’s investment patterns. As I pen this article, Malaysia’s coastal state of Penang becomes the talk of the town, with a surge in high-tech investments that threaten to outpace even China’s most booming cities. What makes this surprising destination so attractive to the world’s leading semiconductor companies?
The US Push for Allied Action against China's Advanced Chip
As the race for technological superiority intensifies, the semiconductor industry has emerged as a critical battleground. The US, a leader in this field, faces growing concerns about China’s rapid development of advanced chips and the potential national security risks they pose. In response, the US is urging its allies, including Japan, South Korea, and the Netherlands, to take more robust actions to prevent their companies from contributing to China’s advanced chip development.
FlexAI Aims to Revolutionise AI Compute Infrastructure
FlexAI is a French startup spearheading a mission to revolutionise AI compute infrastructure. The challenge I aim to tackle in this article is the intricacies and demands that developers face when managing AI compute infrastructure. The current state of affairs is far removed from the simplicity of deploying applications in the general-purpose cloud. Developers grapple with hardware selection, interconnectivity, and managing complex software ecosystems – a stark contrast to the straightforward process of spinning up instances in the general-purpose cloud.
Big Tech's Investment and Its Economic Ramifications
The most influential tech firms have set their sights on leading the charge. In recent earnings reports, behemoths such as Google, Microsoft, and Meta have emphasised their multi-billion-dollar commitments to AI research and development, raising questions about the motivations behind these investments and their potential implications for the wider economy.
Will AI Drive a Supercycle for Desktop and Laptop Sales
As artificial intelligence (AI) transforms technology, the PC industry ponders whether this innovation will drive a “supercycle” for desktop and laptop sales in the coming year. This piece examines the potential impact of AI through the lens of consumer market dynamics. For decades, consumers have shaped PC sales trends. Their purchasing decisions hold significant weight in the industry. In considering the role of AI in driving a potential sales surge, it is crucial to consider recent consumer patterns.
Technology Companies Face a Storm of Challenges
As the tech earnings season unfolds, the industry’s heavyweights, including Tesla, Meta, Alphabet (Google), and Microsoft, prepare to face a potent mix of opportunities and challenges. Amid the backdrop of a burgeoning generative AI market predicted to reach trillion-dollar revenues within the next decade, and a volatile investor sentiment, each company carries a distinctive set of issues.
Nova AI Redefines End-to-End Code Testing for SMEs
As software development becomes increasingly agile and continuous, code testing has emerged as a critical component of the development process. With the advent of generative AI, code testing has become more efficient and effective than ever before. Among the recent generative AI startups offering code testing solutions, Nova AI stands out with its unique approach to end-to-end code testing for mid-size enterprises.
What Is the Path to Profitability for Meta's AI Ambitions
Investors have grown increasingly concerned about Meta’s strategic plans for monetizing its multi-billion dollar investments in generative artificial intelligence (AI). The social media giant’s CEO, Mark Zuckerberg, has acknowledged that returns on these investments will take “considerable time.” However, as a tech industry analyst, I believe it’s essential to scrutinize the path to profitability for Meta’s AI ambitions.
Snowflake Has Its Own Model Now: Arctic LLM
As the market for enterprise-grade generative AI models gains momentum, Snowflake’s offering, Arctic LLM, has recently come to the fore. But what particular roles does Arctic LLM assume in the enterprise sector and how does it stack up against major competitors?
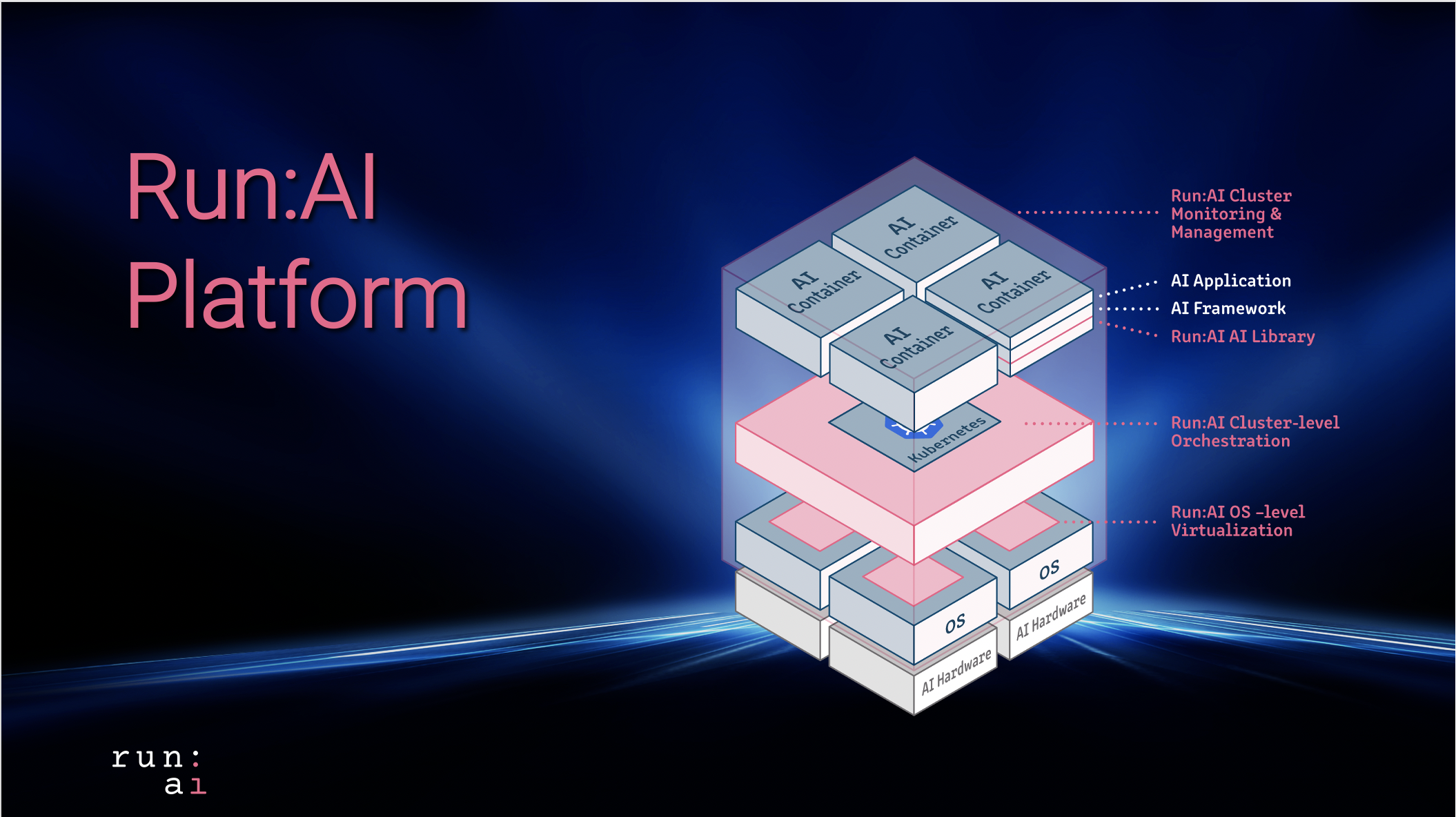
Nvidia Acquires Run:ai to Tackle AI Infrastructure Challenges
Nvidia announced its acquisition of Run:ai, a Tel Aviv-based company specializing in managing and optimizing AI hardware infrastructure. This strategic bet comes at a time when AI workloads are becoming increasingly complex, and the need for sophisticated solutions to manage and optimize resources is paramount.
Intuit's Artificial Intelligence-Driven Growth
Intuit is experiencing a surge in investor enthusiasm, fuelled by the artificial intelligence (AI) boom. The company’s stock has gained nearly 40% over the past 12 months, outpacing the S&P 500’s growth, and surpassing the market capitalization of major investment banks like Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, and Citigroup. But what sets Intuit apart from its competitors is its successful integration of AI into its core offerings.
Generative AI's Financial Impact on Tech Companies
As the race to harness the power of generative AI gathers steam in the tech industry, a dose of reality is needed. Yes, AI models that can generate text, images, and video with human-like output are impressive. But what’s the practical business value of these AI advancements, and how is it reflected in the financial statements of major tech companies?
Texture: Data Collection Platform for Renewable Energy
In the pursuit of a sustainable future, the growing renewable energy sector is poised to lead the charge, but it faces a critical challenge: interoperability. As solar, wind, and battery installations proliferate, fragmentation and communication barriers arise, stymieing growth and preventing the industry from realising its full potential. Enter Texture, a game-changing platform on a mission to break down those barriers and unlock the sector’s untapped potential.